Navigator: registerProtocolHandler() method
Secure context: This feature is available only in secure contexts (HTTPS), in some or all supporting browsers.
The Navigator method registerProtocolHandler() lets websites register their ability to open or handle particular URL schemes (aka protocols).
For example, this API lets webmail sites open mailto: URLs, or VoIP sites open tel: URLs.
Syntax
registerProtocolHandler(scheme, url)
Parameters
scheme-
A string containing the permitted scheme for the protocol that the site wishes to handle. For example, you can register to handle SMS text message links by passing the
"sms"scheme. url-
A string containing the URL of the handler. This URL must include
%s, as a placeholder that will be replaced with the escaped URL to be handled.Note: The handler URL must use the
httpsscheme. Older browsers also supportedhttp.
Return value
None (undefined).
Exceptions
SecurityErrorDOMException-
The user agent blocked the registration. This might happen if:
- The registered scheme (protocol) is invalid, such as a scheme the browser handles itself (
https:,about:, etc.) - The handler URL's origin does not match the origin of the page calling this API.
- The browser requires that this function is called from a secure context.
- The browser requires that the handler's URL be over HTTPS.
- The registered scheme (protocol) is invalid, such as a scheme the browser handles itself (
SyntaxErrorDOMException-
The
%splaceholder is missing from the handler URL.
Permitted schemes
For security reasons, registerProtocolHandler() restricts which schemes can be registered.
A custom scheme may be registered as long as:
- The custom scheme's name begins with
web+ - The custom scheme's name includes at least 1 letter after the
web+prefix - The custom scheme has only lowercase ASCII letters in its name.
For example, web+burger, as shown in the Example below.
Otherwise, the scheme must be one of the following:
bitcoinftpftpsgeoimircircsmagnetmailtomatrixmmsnewsnntpopenpgp4fprsftpsipsmssmstosshtelurnwebcalwtaixmpp
Examples
If your site is burgers.example.com, you can register a protocol handler for it to handle web+burger: links, like so:
navigator.registerProtocolHandler(
"web+burger",
"https://burgers.example.com/?burger=%s",
);
This creates a handler that lets web+burger: links send the user to your site, inserting the accessed burger URL into the %s placeholder.
This script must be run from the same origin as the handler URL (so any page at https://burgers.example.com), and the handler URL must be http or https.
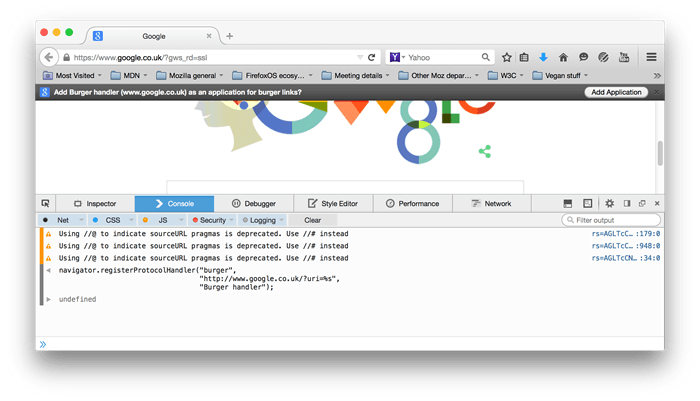
The user will be notified that your code asked to register the protocol handler, so that they can decide whether or not to allow it. See the screenshot below for an example on google.co.uk:
Specifications
| Specification |
|---|
| HTML Standard # custom-handlers |
Browser compatibility
BCD tables only load in the browser