数学
Math 命名空间对象包含数学常量和函数的静态属性和方法。
¥The Math namespace object contains static properties and methods for mathematical constants and functions.
Math 与 Number 型配合使用。它不适用于 BigInt。
¥Math works with the Number type. It doesn't work with BigInt.
描述
¥Description
与大多数全局对象不同,Math 不是构造函数。你不能将其与 new 运算符 一起使用或将 Math 对象作为函数调用。Math 的所有属性和方法都是静态的。
¥Unlike most global objects, Math is not a constructor. You cannot use it with the new operator or invoke the Math object as a function. All properties and methods of Math are static.
注意:许多
Math函数的精度取决于实现。¥Note: Many
Mathfunctions have a precision that's implementation-dependent.这意味着不同的浏览器可以给出不同的结果。即使相同的 JavaScript 引擎在不同的操作系统或架构上也会给出不同的结果!
¥This means that different browsers can give a different result. Even the same JavaScript engine on a different OS or architecture can give different results!
静态属性
¥Static properties
Math.E-
欧拉数和自然对数的底;大约
2.718。 Math.LN10-
10的自然对数;大约2.303。 Math.LN2-
2的自然对数;大约0.693。 Math.LOG10E-
E的以 10 为底的对数;大约0.434。 Math.LOG2E-
E的以 2 为底的对数;大约1.443。 Math.PI-
圆的周长与其直径的比率;大约
3.14159。 Math.SQRT1_2-
1/2 的平方根;大约
0.707。 Math.SQRT2-
2的平方根;大约1.414。 Math[Symbol.toStringTag]-
[Symbol.toStringTag]属性的初始值为字符串"Math"。该属性在Object.prototype.toString()中使用。
静态方法
¥Static methods
Math.abs()-
返回输入的绝对值。
Math.acos()-
返回输入的反余弦。
Math.acosh()-
返回输入的双曲反余弦。
Math.asin()-
返回输入的反正弦。
Math.asinh()-
返回数字的双曲反正弦。
Math.atan()-
返回输入的反正切。
Math.atan2()-
返回其参数商的反正切值。
Math.atanh()-
返回输入的双曲反正切。
Math.cbrt()-
返回输入的立方根。
Math.ceil()-
返回大于或等于输入的最小整数。
Math.clz32()-
返回 32 位整数输入的前导零位数。
Math.cos()-
返回输入的余弦。
Math.cosh()-
返回输入的双曲余弦。
Math.exp()-
返回 ex,其中 x 是参数,e 是欧拉数(
2.718…,自然对数的底数)。 Math.expm1()-
返回从
exp(x)减去1。 Math.floor()-
返回小于或等于输入的最大整数。
Math.f16round()-
返回输入的最接近的 半精度 浮点表示。
Math.fround()-
返回输入的最接近的 单精度 浮点表示。
Math.hypot()-
返回其参数平方和的平方根。
Math.imul()-
返回输入的 32 位整数乘法的结果。
Math.log()-
返回输入的自然对数(㏒e;也称为㏑)。
Math.log10()-
返回输入的以 10 为底的对数。
Math.log1p()-
返回数字
x的1 + x的自然对数(㏒e;也为㏑)。 Math.log2()-
返回输入的以 2 为底的对数。
Math.max()-
返回零个或多个数字中最大的一个。
Math.min()-
返回零个或多个数字中的最小值。
Math.pow()-
返回底数
x的指数幂y(即xy)。 Math.random()-
返回
0和1之间的伪随机数。 Math.round()-
返回输入四舍五入到最接近的整数的值。
Math.sign()-
返回输入的符号,表示它是正数、负数还是零。
Math.sin()-
返回输入的正弦值。
Math.sinh()-
返回输入的双曲正弦。
Math.sqrt()-
返回输入的正平方根。
Math.tan()-
返回输入的正切值。
Math.tanh()-
返回输入的双曲正切。
Math.trunc()-
返回输入的整数部分,删除任何小数位。
示例
度数和弧度之间的转换
¥Converting between degrees and radians
三角函数 sin()、cos()、tan()、asin()、acos()、atan() 和 atan2() 期望(和返回)以弧度为单位的角度。
¥The trigonometric functions sin(), cos(), tan(), asin(), acos(), atan(), and atan2() expect (and return) angles in radians.
由于人类倾向于以度为单位进行思考,并且某些函数(例如 CSS 变换)可以接受度,因此最好保留在两者之间进行转换的函数:
¥Since humans tend to think in degrees, and some functions (such as CSS transforms) can accept degrees, it is a good idea to keep functions handy that convert between the two:
function degToRad(degrees) {
return degrees * (Math.PI / 180);
}
function radToDeg(rad) {
return rad / (Math.PI / 180);
}
计算等边三角形的高度
¥Calculating the height of an equilateral triangle
如果我们要计算等边三角形的高,并且已知其边长为 100,则可以使用以下公式:相邻边的长度乘以角的正切值等于相反数。
¥If we want to calculate the height of an equilateral triangle, and we know its side length is 100, we can use the formulae length of the adjacent multiplied by the tangent of the angle is equal to the opposite.
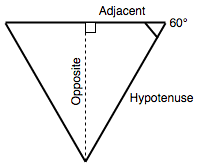
在 JavaScript 中,我们可以使用以下代码来做到这一点:
¥In JavaScript, we can do this with the following:
50 * Math.tan(degToRad(60));
我们使用 degToRad() 函数将 60 度转换为弧度,因为 Math.tan() 需要以弧度为单位的输入值。
¥We use our degToRad() function to convert 60 degrees to radians, as Math.tan() expects an input value in radians.
返回两个边界之间的随机整数
¥Returning a random integer between two bounds
这可以通过 Math.random() 和 Math.floor() 的组合来实现:
¥This can be achieved with a combination of Math.random() and Math.floor():
function random(min, max) {
const num = Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min;
return num;
}
random(1, 10);
规范
| Specification |
|---|
| ECMAScript Language Specification # sec-math-object |
浏览器兼容性
BCD tables only load in the browser
也可以看看
¥See also